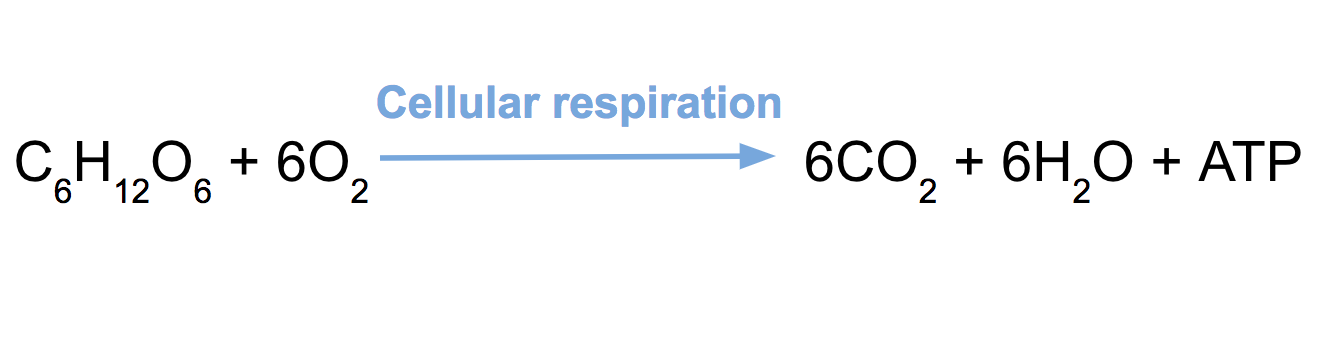
Most of the ATP produced by aerobic cellularrespiration is made by oxidative phosphorylation. The energy released is used to create a chemiosmotic potential by pumping protons across a membrane. This potential is then used to drive ATP synthase and produce ATP from ADP and a phosphate group. · Learn the chemical equation for cellular respiration, the process that converts glucose and oxygen into water, carbon dioxide and ATP. Find out the four stages of respiration and how fats and proteins can also produce ATP. Most of the ATP produced by aerobic cellularrespiration is made by oxidative phosphorylation. The energy released is used to create a chemiosmotic potential by pumping protons across a membrane. This potential is then used to drive ATP synthase and produce ATP from ADP and a phosphate group. What is the chemical equation for cellular respiration?The overall chemical equation for aerobic cellular respiration, which requires oxygen, provides a concise summary of this complex process: C₆H₁₂O₆ + 6O₂ → 6CO₂ + 6H₂O + Energy (ATP). This formula illustrates the reactants consumed and the products generated. Glucose (C₆H₁₂O₆) serves as the primary fuel source for cellular respiration.What is cellular respiration?Cellular respiration is the process of using oxygen to break down sugar to release energy in the form of Adenosine triphosphate (ATP). ATP is then used for muscle movement, building cells and other cell functions.How many units of ATP are produced during cellular respiration?During cellular respiration, one glucose molecule combines with six oxygen molecules to produce water, carbon dioxide and 38 units of ATP. The chemical formula for the overall process is: C 6 H 12 O 6 + 6O 2 –> 6CO 2 + 6H 2 O + 36 or 38 ATP Glucose, a complex sugar, combines with oxygen during respiration to produce water, carbon dioxide and ATP.How many stages of cellular respiration are there?Respiration proceeds in four discrete stages and releases about 39 percent of the energy stored in the glucose molecules. Although the main process of cellular respiration is essentially an oxidation reaction, four things have to happen, so you can make the full potential amount of ATP.cellular respiration, the process by which organisms combine oxygen with foodstuff molecules, diverting the chemical energy in these substances into life-sustaining activities and discarding, as waste products, carbon dioxide and water. Organisms that do not depend on oxygen degrade foodstuffs in a process called fermentation. (For longer treatment...See full list on britannica.comOne objective of the degradation of foodstuffs is to convert the energy contained in chemical bonds into the energy-rich compound adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which captures the chemical energy obtained from the breakdown of food molecules and releases it to fuel other cellular processes. In eukaryotic cells (that is, any cells or organisms that p...See full list on britannica.comBiologists differ somewhat with respect to the names, descriptions, and the number of stages of cellular respiration. The overall process, however, can be distilled into three main metabolic stages or steps: glycolysis, the tricarboxylic acid cycle (TCA cycle), and oxidative phosphorylation (respiratory-chain phosphorylation).See full list on britannica.comGlycolysis (which is also known as the glycolytic pathway or the Embden-Meyerhof-Parnas pathway) is a sequence of 10 chemical reactions taking place in most cells that breaks down a glucose molecule into two pyruvate (pyruvic acid) molecules. Energy released during the breakdown of glucose and other organic fuel molecules from carbohydrates, fats, ...See full list on britannica.comThe TCA cycle (which is also known as the Krebs, or citric acid, cycle) plays a central role in the breakdown, or catabolism, of organic fuel molecules. The cycle is made up of eight steps catalyzed by eight different enzymes that produce energy at several different stages. Most of the energy obtained from the TCA cycle, however, is captured by the...See full list on britannica.comIn the oxidative phosphorylation stage, each pair of hydrogen atoms removed from NADH and FADH2 provides a pair of electrons that—through the action of a series of iron-containing hemoproteins, the cytochromes—eventually reduces one atom of oxygen to form water. In 1951 it was discovered that the transfer of one pair of electrons to oxygen results in the formation of three molecules of ATP.Are you a student? Get Britannica Premium for only 24.95 - a 67% discount!Learn MoreOxidative phosphorylation is the major mechanism by which the large amounts of energy in foodstuffs are conserved and made available to the cell. The series of steps by which electrons flow to oxygen permits a gradual lowering of the energy of the electrons. This part of the oxidative phosphorylation stage is sometimes called the electron transport chain. Some descriptions of cellular respiration that focus on the importance of the electron transport chain have changed the name of the oxidative phosphorylation stage to the electron transport chain.See full list on britannica.comFeb 3, 2025 · Learn the chemical equation for cellular respiration, the process of generating ATP from glucose and oxygen. Explore the stages of glycolysis, Krebs cycle, and electron transport chain, and the differences between aerobic and anaerobic respiration. · The overall chemical equation for aerobic cellular respiration, which requires oxygen, provides a concise summary of this complex process: C₆H₁₂O₆ + 6O₂ → 6CO₂ + 6H₂O + Energy (ATP). View all Cellular respiration involves many chemical reactions, but they can all be summed up with this chemical equation: CO 2 + 6 H + Energy where the energy that is released is in chemical energy in ATP (vs. thermal energy as heat). The equation for cellular respiration is: C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O + Energy This represents glucose (C6H12O6) and oxygen (6O2) being converted into carbon dioxide (6CO2), water (6H2O), and energy. cellular respiration, the process by which organisms combine oxygen with foodstuff molecules, diverting the chemical energy in these substances into life-sustaining activities and discarding, as waste products, carbon dioxide and water. Organisms that do not depend on oxygen degrade foodstuffs in a process called fermentation. (For longer treatment...See full list on britannica.comOne objective of the degradation of foodstuffs is to convert the energy contained in chemical bonds into the energy-rich compound adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which captures the chemical energy obtained from the breakdown of food molecules and releases it to fuel other cellular processes. In eukaryotic cells (that is, any cells or organisms that p...See full list on britannica.comBiologists differ somewhat with respect to the names, descriptions, and the number of stages of cellular respiration. The overall process, however, can be distilled into three main metabolic stages or steps: glycolysis, the tricarboxylic acid cycle (TCA cycle), and oxidative phosphorylation (respiratory-chain phosphorylation).See full list on britannica.comGlycolysis (which is also known as the glycolytic pathway or the Embden-Meyerhof-Parnas pathway) is a sequence of 10 chemical reactions taking place in most cells that breaks down a glucose molecule into two pyruvate (pyruvic acid) molecules. Energy released during the breakdown of glucose and other organic fuel molecules from carbohydrates, fats, ...See full list on britannica.comThe TCA cycle (which is also known as the Krebs, or citric acid, cycle) plays a central role in the breakdown, or catabolism, of organic fuel molecules. The cycle is made up of eight steps catalyzed by eight different enzymes that produce energy at several different stages. Most of the energy obtained from the TCA cycle, however, is captured by the...See full list on britannica.comIn the oxidative phosphorylation stage, each pair of hydrogen atoms removed from NADH and FADH2 provides a pair of electrons that—through the action of a series of iron-containing hemoproteins, the cytochromes—eventually reduces one atom of oxygen to form water. In 1951 it was discovered that the transfer of one pair of electrons to oxygen results in the formation of three molecules of ATP.Are you a student? Get Britannica Premium for only 24.95 - a 67% discount!Learn MoreOxidative phosphorylation is the major mechanism by which the large amounts of energy in foodstuffs are conserved and made available to the cell. The series of steps by which electrons flow to oxygen permits a gradual lowering of the energy of the electrons. This part of the oxidative phosphorylation stage is sometimes called the electron transport chain. Some descriptions of cellular respiration that focus on the importance of the electron transport chain have changed the name of the oxidative phosphorylation stage to the electron transport chain.See full list on britannica.comFeb 3, 2025 · Learn the chemical equation for cellular respiration, the process of generating ATP from glucose and oxygen. Explore the stages of glycolysis, Krebs cycle, and electron transport chain, and the differences between aerobic and anaerobic respiration. · The overall chemical equation for aerobic cellular respiration, which requires oxygen, provides a concise summary of this complex process: C₆H₁₂O₆ + 6O₂ → 6CO₂ + 6H₂O + Energy (ATP). View all Cellular respiration involves many chemical reactions, but they can all be summed up with this chemical equation: CO 2 + 6 H + Energy where the energy that is released is in chemical energy in ATP (vs. thermal energy as heat). The equation for cellular respiration is: C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O + Energy This represents glucose (C6H12O6) and oxygen (6O2) being converted into carbon dioxide (6CO2), water (6H2O), and energy. · The overall chemical equation for aerobic cellular respiration, which requires oxygen, provides a concise summary of this complex process: C₆H₁₂O₆ + 6O₂ → 6CO₂ + 6H₂O + Energy (ATP). Cellular respiration involves many chemical reactions, but they can all be summed up with this chemical equation: CO 2 + 6 H + Energy where the energy that is released is in chemical energy in ATP (vs. thermal energy as heat). The equation for cellular respiration is: C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O + Energy This represents glucose (C6H12O6) and oxygen (6O2) being converted into carbon dioxide (6CO2), water (6H2O), and energy. The word equationforcellularrespiration is glucose sugar oxygen carbon dioxide water energy as ATP. Rephrase the function of cellularrespiration in your own words. Eighth graders who have a better handle on cellularrespiration should be able to. CellularRespirationEquations. Cellularrespiration can be written as chemical equations. An example of the aerobic respirationequation is in Figure 3. CellularRespirationEquation with Carbons and Hydrogens.CellularRespirationEquation, Types, Stages, Products & Diagrams. Glycolysis Flow Diagram: Understanding CellularRespiration Process. What is the correct equationforcellularrespiration?What are the products of cellularrespiration? Glucose and oxygen. Carbon dioxide, water, ATP. Write a similar equationforcellularrespiration (Be sure to include a description of the form of energy).The chemical equationforcellularrespiration is widely accepted in biology and is foundational in studies related to energy transformation in living organisms. In cellularrespiration, glucose and oxygen are the initial reactants. Glucose, derived from carbohydrates, acts as the fuel source, while oxygen serves as the final electron acceptor. The equationforcellularrespiration is essentially the equationfor photosynthesis backwards. Photosynthesis occurs within a chloroplast and uses chlorophyll to absorb the light energy that is necessary to fuel the following equation. What "products" does cellularrespiration create? Why is ATP so important for our bodies? How can students easily remember the word equationforcellularrespiration?Forcellularrespiration, the full equation looks like this: Glucose + Oxygen → Carbon Dioxide + Water + Energy (ATP). Aerobic cellularrespiration is a combustion reaction. How does the equationfor photosynthesis relate to the equationforcellularrespiration?Cellularrespiration is the process by which cells generate energy from glucose molecules. All organisms must go through cellularrespiration. C 6 h 12 o 6 + 6 o 2 → 6 co 2 + 6 h 2 o + energy (as atp) the word equationfor this is: But cellularrespiration, let's us go from glucose to energy and some other byproducts. Inputs & Outputs: CellularRespiration V Explore Photosynthesis and CellularRespiration are both important processes in living things. They are chemical reactions.Chlorophyll Word Bank Radiant energy Chemical energy 3. What is the chemical equationfor photosynthesis? 4. Write the balanced equationforcellularrespiration. 5. Which process is a constructing process and which is a breaking down process. The chemical equationforcellularrespiration can be expressed as followsCellularrespiration is the process of converting glucose and oxygen into energy, and its equation is: C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O + ATP. Aerobic respiration occurs in the mitochondria, while anaerobic respiration occurs in the cytoplasm of the cell.Photosynthesis allows forcellularrespiration to occur because it creates glucose, a reactant in the equationforcellularrespiration.