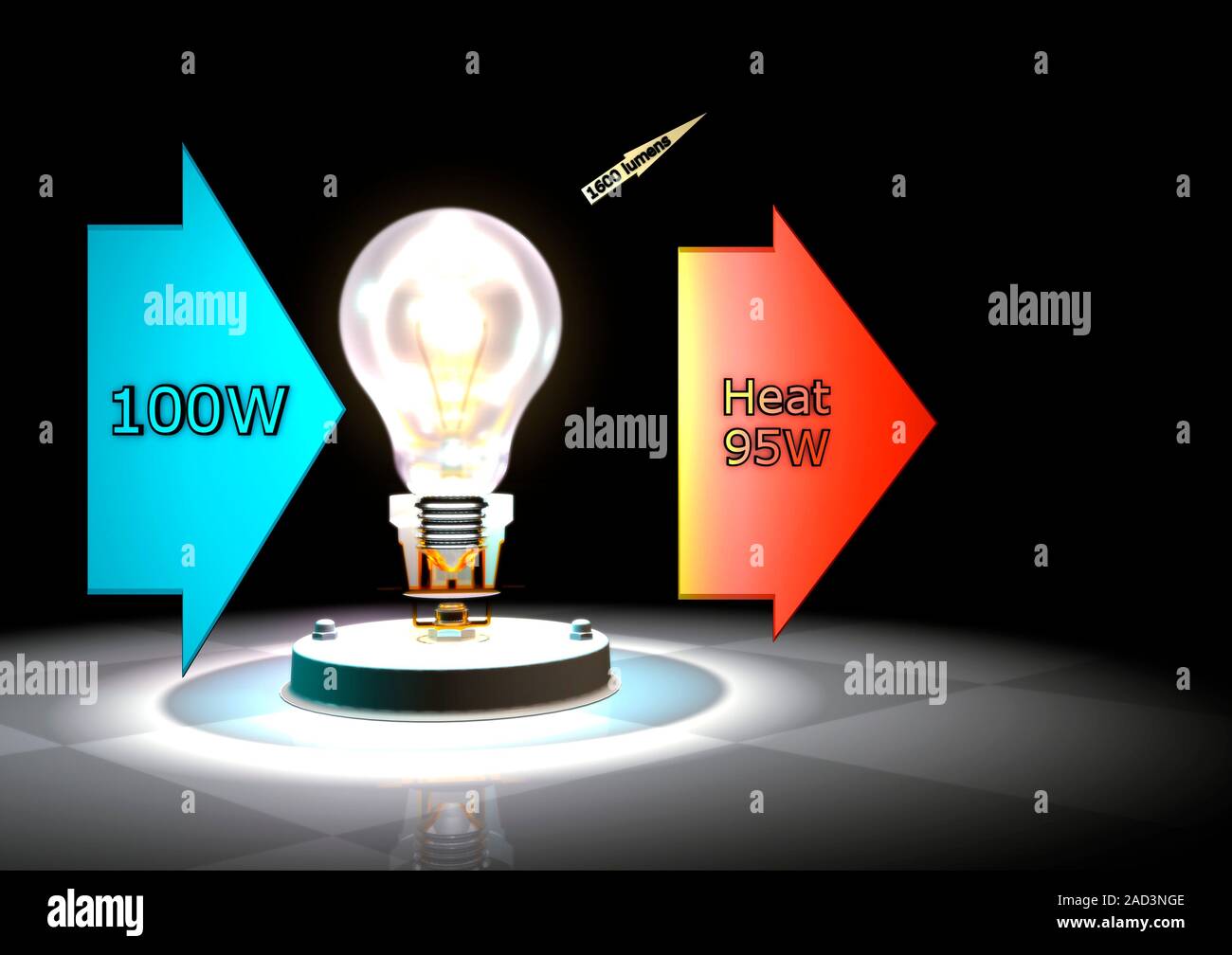
· Incandescent bulb energy efficiency remains very low in 2025. Most incandescent bulbs convert only about 2% of electrical energy into visible light, with the rest lost as heat. In this exercise, students will use a light to demonstrate the difference between being energy-efficient and energy-wasteful, and learn what energyefficiency means. Incandescent technology produces light by heating up a metal filament enclosed within the lamp’s glass. More than ninety percent of the energy used by an incandescent light bulb escapes as heat, with less than 10% producing light. Incandescents are the most commonly found bulbs in American homes. · Replacing one incandescentbulb with an LED can lower energy use by about 75%. This leads to less electricity generation and fewer greenhouse gas emissions. Every choice counts. By opting for LED lighting, you play a crucial role in environmental conservation and achieving global sustainability goals. · Compare LED, CFL, and incandescentbulbs for cost, performance, and energy savings. See which bulb saves you the most — backed by DOE data. · Incandescent bulbs lose 90% of their energy as heat, which means they’re the least efficient overall. CFLs aren’t much better, as they lose about 80% of their energy as heat. LEDs, meanwhile, lose a maximum of 20% of their energy as heat. · Incandescent light bulbs convert a significant portion of energy into heat rather than light. LED light bulbs are designed for higher energyefficiency compared to incandescent options. The technology behind incandescentbulbs relies on heating a filament, which consumes more electricity.